Kopernisium
unsur kimia dengan lambang Cn dan nomor atom 112
(Dialihkan dari Cn (unsur kimia))
Kopernisium (hingga 19 Februari 2010 memiliki nama sementara ununbium) adalah suatu unsur kimia dalam tabel periodik yang memiliki lambang Cn (sebelumnya Uub) dan nomor atom 112. Unsur 112 tergolong unsur yang sangat berat. Jika mengikuti kecenderungan pada tabel periodik, seharusnya wujudnya berupa metal cair yang lebih volatil (mudah menguap) daripada raksa.
112Cn Kopernisium | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
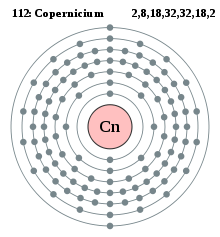 Konfigurasi elektron kopernisium | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sifat umum | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pengucapan | /kopêrnisium/ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kopernisium dalam tabel periodik | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nomor atom (Z) | 112 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Golongan | golongan 12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Periode | periode 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Blok | blok-d | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kategori unsur | logam transisi, pernah dipertimbangkan sebagai logam miskin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nomor massa | [285] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Konfigurasi elektron | [Rn] 5f14 6d10 7s2 (diprediksi)[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elektron per kelopak | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 2 (diprediksi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sifat fisik | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fase pada STS (0 °C dan 101,325 kPa) | cair (diprediksi) [2][3] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Titik lebur | 283 ± 11 K (10 ± 11 °C, 50 ± 20 °F) (diprediksi)[3] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Titik didih | 340 ± 10 K (67 ± 10 °C, 153 ± 18 °F)[3] (diprediksi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kepadatan mendekati s.k. | 14,0 g/cm3 (diprediksi)[3] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Titik tripel | 283 K, 25 kPa (diprediksi)[3] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sifat atom | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bilangan oksidasi | 0, (+1), +2, (+4), (+6) (tanda kurung: prediksi)[1][4][5][6] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Energi ionisasi | ke-1: 1155 kJ/mol ke-2: 2170 kJ/mol ke-3: 3160 kJ/mol (artikel) (semuanya merupakan perkiraan)[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jari-jari atom | perhitungan: 147 pm[1][5] (diprediksi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jari-jari kovalen | 122 pm (diprediksi)[7] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lain-lain | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kelimpahan alami | sintetis | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Struktur kristal | susunan padat heksagon (hcp) (diprediksi)[3] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nomor CAS | 54084-26-3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sejarah | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Penamaan | dari N. Copernicus | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Penemuan | Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung (1996) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isotop kopernisium yang utama | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Ununbium secara resmi dinamakan Kopernisium dengan simbol Cn pada ulang tahun ke 537 Nicolaus Copernicus oleh IUPAC.
Referensi
sunting- ^ a b c d Hoffman, Darleane C.; Lee, Diana M.; Pershina, Valeria (2006). "Transactinides and the future elements". Dalam Morss; Edelstein, Norman M.; Fuger, Jean. The Chemistry of the Actinide and Transactinide Elements (edisi ke-3). Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer Science+Business Media. ISBN 978-1-4020-3555-5.
- ^ Soverna S 2004, 'Indication for a gaseous element 112,' in U Grundinger (ed.), GSI Scientific Report 2003, GSI Report 2004-1, p. 187, ISSN 0174-0814
- ^ a b c d e f Mewes, J.-M.; Smits, O. R.; Kresse, G.; Schwerdtfeger, P. (2019). "Copernicium is a Relativistic Noble Liquid". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. doi:10.1002/anie.201906966.
- ^ Gäggeler, Heinz W.; Türler, Andreas (2013). "Gas Phase Chemistry of Superheavy Elements". The Chemistry of Superheavy Elements. Springer Science+Business Media. hlm. 415–483. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-37466-1_8. ISBN 978-3-642-37465-4. Diakses tanggal 16 Juli 2022.
- ^ a b Fricke, Burkhard (1975). "Superheavy elements: a prediction of their chemical and physical properties". Recent Impact of Physics on Inorganic Chemistry. Structure and Bonding. 21: 89–144. doi:10.1007/BFb0116498. ISBN 978-3-540-07109-9. Diakses tanggal 16 Juli 2022.
- ^ Hu, Shu-Xian; Zou, Wenli (23 September 2021). "Stable copernicium hexafluoride (CnF6) with an oxidation state of VI+". Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. 2022 (24): 321–325. doi:10.1039/D1CP04360A.
- ^ Chemical Data. Copernicium - Cn, Royal Chemical Society
- ^ Utyonkov, V. K.; Brewer, N. T.; Oganessian, Yu. Ts.; et al. (30 Januari 2018). "Neutron-deficient superheavy nuclei obtained in the 240Pu+48Ca reaction". Physical Review C. 97 (14320): 1–10. Bibcode:2018PhRvC..97a4320U. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.97.014320.
- ^ Chart of Nuclides. Brookhaven National Laboratory
- ^ Såmark-Roth, A.; Cox, D. M.; Rudolph, D.; et al. (2021). "Spectroscopy along Flerovium Decay Chains: Discovery of 280Ds and an Excited State in 282Cn". Physical Review Letters. 126: 032503. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.126.032503.
Pranala luar
sunting- IUPAC Diarsipkan 2010-02-24 di Wayback Machine.
